The rise of deepfake technology in recent years has been a cause of concern for individuals and institutions worldwide.
These manipulated images can cause significant harm, from spreading misinformation to damaging reputations or even impacting national security.
To combat this growing threat, companies have turned to face liveness detection – a powerful biometric authentication tool that aims to detect and prevent deepfake attacks. Liveness detection technology is a staple component in many biometrics authentication systems (e.g. fingerprint scanning) and it serves as one of the most essential components in fraud detection and fraud prevention.
What Are Deepfakes?
Deepfakes are sophisticated manipulations of audio and video content that use artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to convincingly superimpose one person’s likeness onto another — resulting in seemingly authentic but entirely fabricated footage.
A notable example of deepfake manipulation is shown in the video below. It features former United States President, Barack Obama (or rather his likeness) delivering a speech that he has never delivered before.
With regard to the identity verification industry, deepfake fraud is a manipulation technique used by fraudsters to impersonate an individual’s identity. These impersonations can then be used to commit identity fraud by gaining unauthorised access to a victim’s personal accounts, encrypted data, and other restricted mediums.
In what is known as Deepfake audio, voice impersonations can also be done by manipulating the voice samples of a targeted individual. Fragments of a victim’s voice are extracted and run through a modifier to replicate the original voice of the victim.
How Are Deepfakes Made?
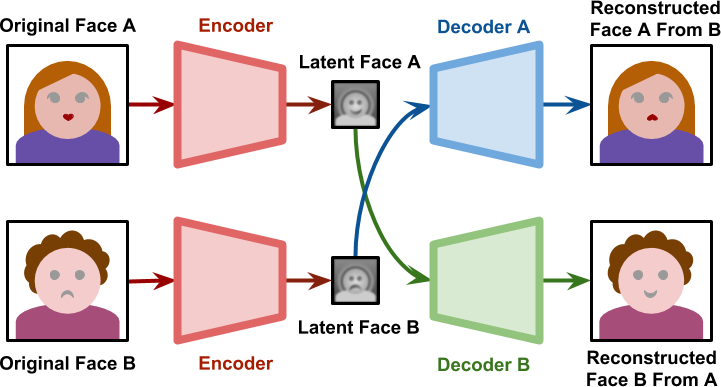
Several steps are involved in creating a Deepfake image/video. Firstly, an AI algorithm known as an encoder is used to process thousands of face shots of the two individuals. The artificial intelligence identifies and learns the common features shared between the faces while compressing the images. Subsequently, a second AI algorithm called a decoder is trained to reconstruct the faces from the compressed images.
Since the faces are distinct, one decoder is trained to restore the first person’s face, while another decoder is trained for the second person’s face. To execute the face swap, the encoded images are inputted into the “incorrect” decoder. For instance, a compressed image of person A’s face is fed into the decoder trained on person B.
The decoder then reconstructs Person B’s face with the expressions and orientation of Person A. This process needs to be repeated for each frame to achieve a convincing Deepfake face-swap video.
What Is Liveness Detection?
Facial liveness detection, also known as presentation attack detection or deepfake detection, is a critical component used in many facial recognition systems. It involves distinguishing between real and synthetic signals to ensure that the input source is genuine and not a digitally manipulated representation.
While deepfake technology can create highly convincing videos, liveness detection helps verify the “liveness” of a subject by detecting physiological or behavioural characteristics that are difficult to replicate artificially.
How Liveness Detection Works

As part of the facial recognition process, liveness detection systems typically use a combination of sensors and algorithms to detect subtle differences between live and synthetic faces.
Some of the most common liveness detection techniques include:
- Motion Analysis: This method examines the movement of facial features, such as blinking, eye gaze, and natural facial expressions, which are difficult for deepfake algorithms to replicate accurately.
- Texture Analysis: By scrutinizing the fine details in the skin texture and pores, liveness detection algorithms can differentiate between a real human face and a digitally generated one, which may lack the subtle variations found in authentic skin.
- Thermal Imaging: Using infrared cameras, this approach measures heat emissions from the subject’s face, as real human skin emits heat differently than synthetic materials, like silicone masks, used in deepfake creation.
- 3D Depth Analysis: By employing depth-sensing technologies like structured light or time-of-flight cameras, liveness detection systems can capture the 3D geometry of a face and identify subtle differences between a live person and a flat, 2D image or video.
- Behavioural Analysis: This approach focuses on the subject’s natural behavioural patterns, such as speech patterns, blinking frequencies, and head movements, to detect anomalies that might indicate a deepfake.
How Does Liveness Detection Combat Deepfake Attacks
Liveness detection can be used to detect and prevent deepfake attacks in a number of ways. For example, liveness detection systems can be used to:
- Authenticate Users: Liveness detection systems can be used to authenticate users who are logging into a website or app. This can help to prevent unauthorised access by deepfakes.
- Prevent Fraud: Liveness detection systems can be used to prevent fraud, such as insurance fraud or credit card fraud. This can be done by requiring users to perform a liveness check before they can complete a transaction.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Liveness detection systems can be used to protect sensitive data, such as medical records or financial information. This can be done by requiring users to perform a liveness check before they can access the data.
Liveness detection is not an ultimate solution to eradicate all deepfake attacks — but it poses a significant defense against potential attackers. Social media platforms, video conferencing tools, and authentication systems can implement liveness detection to ensure that users are genuine and not engaging in harmful activities.
Continuous research and development in liveness detection technologies are vital to counter the ever-evolving techniques employed by deepfake creators.
What Are The Types of Liveness Detection Techniques?
There are two types of liveness detection techniques: active and passive. Active liveness detection requires the user to perform an action. On the other hand, passive liveness detection runs in the background and does not require any input from the user.
 Passive Liveness Detection
Passive Liveness Detection
- Does not require the user to perform any specific actions
- Artificial intelligence is used to analyse a single image of a user
- Runs in the background — sometimes without the user’s knowledge.
- Quicker and more convenient for users as no action is required from them.
- Suitable for services with an emphasis on user experience and convenience.
The scanning process doesn’t impose any action requirements on the user. This allows for reduced friction and as a result; lower instances of user abandonment during remote customer onboarding processes.
Various methods are used during passive liveness detection. This includes evaluating a selfie photograph, recording a video, or even using flashing lights on the person. It uses artificial intelligence models to assess if a biometric template belongs to a live person or not.
 Active Liveness Detection
Active Liveness Detection
In this liveness detection technique, users must respond to prompts that require motions such as smiling and blinking. This method offers increased reliability and accuracy compared to passive liveness detection.
- Requires user action to prevent attackers from using photos, videos, masks, or avatars of the users to spoof the system
- Typically combines motion analysis and artificial intelligence with multiple sets of images
- Usually paired with a challenge-response system for additional security against spoofing attempts. Challenge-response systems refer to the prompts (challenge) that users are required to perform and their actions (response).
- Suitable for services that place a high priority on data security and protection.
Active detection systems are vulnerable to cybercrime due to their unsophisticated machine-learning models. They are easily deceived by presentation attacks using masks, video manipulation, or synthetic voices.
Bypassing active liveness detection can be done with simple methods, such as wearing a printed image of the target person’s face to mimic blinking and trick the biometric system into verifying the wrong identity.
Challenges and Limitations
While liveness detection is a powerful tool, it still faces certain challenges and limitations:
- Adversarial Attacks: An adversarial attack involves presenting a model with inaccurate or misrepresentative data while in the process of training. Deepfake creators may introduce adversarial attacks that can bypass these safeguards.
- High Resource Requirements: Some liveness detection techniques that rely on advanced hardware like thermal imaging or 3D depth sensing, may require significantly more resources — which makes their use less practical for certain applications.
- False Positives and False Negatives: Liveness detection systems may sometimes generate false positives (incorrectly flagging a genuine user) or false negatives (failing to identify a deepfake), leading to user inconvenience or security breaches.
Bottom Line
Liveness detection is a crucial technology in the ongoing battle against deepfake attacks. By analysing facial movements, skin textures, behavioural patterns, and more, liveness detection systems help identify and prevent the spread of synthetic media that could potentially cause harm or deceive users.
Despite the challenges, continuous advancements in this field and collaborations among researchers, developers and policymakers will help to ensure a safer digital environment for all.




